In The Circular Flow Of Goods And Services, What Does The Product Market Represent?
The Circular Menses of Economic Action
The below mentioned article provides an overview on the Round Flow of Economic Action. After reading this article you will learn about: i. Introduction to the Round Period of Economical Activeness 2. The Circular Flow in a Ii-Sector Economic system iii. The Circular Flow in a Three-Sector Economy 4. The Circular Flow in a Four-Sector Economy.
Introduction to the Circular Flow of Economical Activity:
The all pervasive economic problem is that of scarcity which is solved past three institutions (or decision-making agents) of an economy. They are households (or individuals), firms and regime. They are actively engaged in three economical activities of production, consumption and exchange of goods and services. These decision-makers deed and react in such a manner that all economic activities motion in a round menstruation.
Starting time, we discuss their nature and role in controlling.
Households:
Households are consumers. They may be single-individuals or group of consumers taking a joint decision regarding consumption. They may besides exist families. Their ultimate aim is to satisfy the wants of their members with their limited budgets.
Households are the owners of factors of production—land, labour, capital and entrepreneurial power. They sell the services of these factors and receive income in render in the grade of hire, wages, and interest and profit respectively.
Firms:
The term firm is used interchangeably with the term producer in economics. The decision to manufacture appurtenances and services is taken past a house. For this purpose, it employs factors of production and makes payments to their owners. Just equally household'south consumer appurtenances and services to satisfy their wants, similarly firms produce goods and services to make a profit.
The term 'firm' includes articulation stock companies like DCM, TISCO etc., public enterprises like IOC, STC, etc., partnership concerns, cooperative societies, and even small and large trading shops which do not manufacture the commodities they sell.
Authorities:
The government plays a central role in all types of economic systems—capitalist, socialist and mixed. In a backer economy, the government does not interfere. It merely establishes and protects property rights. It sets standards for weights and measures, and the budgetary system.
In a socialist economic system, the role of the government is very extensive. It owns and regulates the entire production and consumption processes of the economy, and fixes prices of goods and services. In a mixed economic system, the government strengthens the market organisation.
It removes its defects by regulating the activities of the private sector and by providing incentives to it. The government also uses resources to produce appurtenances and services itself which are sold to households and firms. These determination-making agents take economic decisions to produce goods and services and to exchange them in guild to consume them for satisfying the wants of the whole economy.
Production, consumption and exchange are the 3 principal activities of the economy. Consumption and product are flows which operate simultaneously and are interrelated and interdependent. Product leads to consumption and consumption necessitates production.
In other words, production is a means (offset) and consumption is the cease of all economic activities. Both product and consumption, in plow, depend upon exchange. Thus these 2 flows are interrelated and interdependent through exchange.
The Circular Flow in a Ii-Sector Economy:
In a simplified economy with only two types of economic agents, households or consumers and business organisation firms, the circular menstruation of economic activity is shown in Figure 10. Consumers and firms are linked through the product market where goods and services are sold. They are also linked through the cistron market where the factors of product are sold and bought.
Consumers and firms have a dual part, and exchange with ane another in ii singled-out ways:
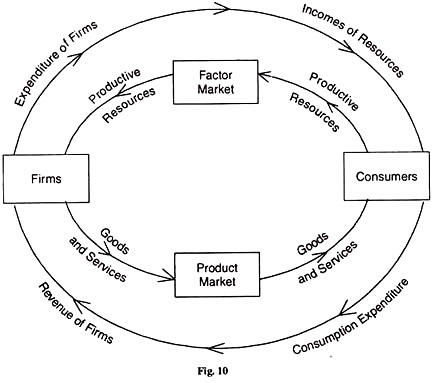
(i) Consumers or households own all the factors of production, that is, country, labour, capital and entrepreneurship, which are as well chosen productive resources. They sell them to firms for producing goods and services.
In the diagram, the sale of appurtenances and services by firms to consumers in the production market is shown in the lower portion of the inner circle from left to right; and the sale of their services to firms by households or consumers in the cistron market is shown in the upper portion of the inner circle from right to left. These are the real flows of goods and services from firms to consumers which are linked with productive resources from consumers to firms through the medium of commutation or barter.
(2) In a modem economic system, exchange takes identify through financial flows which move in the reverse direction to the "real" flows. The buy of appurtenances and services in the product market by consumers is their consumption expenditure which becomes the revenue of the firms and is shown in the outer circle of the lower portion from right to left in the diagram.
The expenditure of firms in buying productive resources in the gene market from the consumers becomes the incomes of households, which is shown in the outer circle of the upper portion from left to right in the diagram.
The Circular Catamenia in a 3-Sector Economy:
So far we have been working on the circular flow of a two-sector model of an economy. To this nosotros add the government sector and then as to make information technology a iii-sector airtight model of round flow of economic activity. For this, we add taxes and government purchases (or expenditure) in our presentation.
Taxes are outflows from the circular menstruum and government purchases are inflows into the circular flow. The circular flow in a 3-sector economic system is illustrated in Effigy 11.
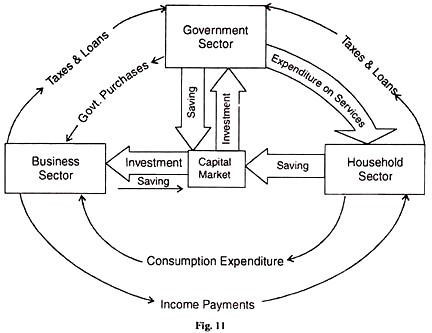
First, accept the circular menstruation between the household sector and the regime sector. Taxes in the form of personal income tax and commodity taxes paid by the household sector are outflows (or leakages) from the circular menses. Only the government purchases the services of the households, makes transfer payments in the course of erstwhile age pensions, unemployment relief, sickness benefit, etc., and likewise spends on them to provide certain social services like didactics, health, housing, water, parks and other facilities.
All such expenditures by the regime are inflows (injections) into the circular flow. Next take the circular menstruum between the concern sector and the authorities sector. All types of taxes paid past the business organization sector to the government are leakages from the circular menses.
On the other hand, the authorities purchases all its requirements of appurtenances of all types from the business sector, gives subsidies and makes transfer payments to firms in order to encourage their production. These authorities expenditures are injections into the circular flow.
Now we have the household, business and government sectors together to show their inflows and outflows in the circular period. As already noted, taxes are a leakage from the round flow. They tend to reduce consumption and saving of the household sector. Reduced consumption, in turn, reduces the sales and incomes of the firms.
On the other hand, taxes on business firms tend to reduce their investment and production. The government offsets these leakages by making purchases from the business sector and buying services of the household sector equal to the amount of taxes. Thus inflows (injections) equal outflows (leakages) in the circular flow.
Figure 11 shows that taxes flow out of the household and business sectors and go to the government. The government purchases appurtenances from firms and also factors of production from households. Thus government purchases of goods and services are an injection in the circular flow and taxes are leakages in the circular flow.
If government purchase exceeds internet taxes then the government will incur a deficit equal to the difference betwixt the two, i.eastward., government expenditure and taxes. The regime finances its arrears by borrowing from the uppercase market which receives funds from the household sector in the form of saving.
On the other manus, if net taxes exceed government purchases the government will take a budget surplus. In this case, the government reduces the public debt and supplies funds to the majuscule market which are received by the business sector.
The Circular Menstruation in a Four-Sector Economy :
And so far the round flow has been shown in the case of a closed economy. But the actual economy is an open up one where strange trade plays an important function. Exports are an injection or inflows into the circular flow of coin. On the other hand, imports are leakages from the circular flow.
They are expenditure southward incurred past the household sector to purchase goods from foreign countries. These exports and imports in the circular flow are shown in Figure 12.
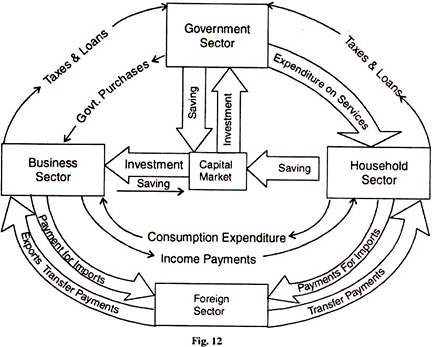
Take the inflows and outflows of the household, business and government sectors in relation to the strange sector. The household sector buys appurtenances imported from abroad and makes payment for them which is a leakage from the round flow of money. The householders' ma receives transfer payments from the strange sector for the services rendered by them in foreign countries.
On the other manus, the business sector exports goods to strange countries and its receipts are an injection in the circular flow or money. Similarly, there are many services rendered by business organisation firms to foreign countries such as shipping, insurance, cyberbanking, etc. for which they receive payments from abroad.
They also receive royalties, interests, dividends, profits, etc. for investments made in foreign countries. On the other paw, the business sector makes payments to the foreign sector for imports о capital appurtenances, machinery, raw materials, consumer appurtenances, and services from abroad. These are the leakages from the round flow of money.
Like the business sector, modern governments also consign and import goods and services, and lend to and borrow from foreign countries. For all exports of goods, the government receives payments from abroad.
Similarly, the government receives payments from foreigners when they visit the country as tourists and for receiving education, etc., and besides when the government provides aircraft, insurance and cyberbanking services to foreigners through the state-owned agencies.
Information technology also receives royalties, interests, dividends, etc. for investments fabricated abroad. These are injections into the round menstruation of money. On the other paw, the leakages are payments made to foreigners for the purchase of goods and services.
Effigy 12 shows the round menses of money of the four sector open economy with saving, taxes and imports shown as leakages from the circular menstruum on the right hand side of figure, and investment, government purchases and exports as injections into the round period, on the left side of the effigy.
Further, imports, exports and transfer payments have been shown to arise from the three domestic sectors—the household, the business and the government. These outflows and inflows ass through the strange sector which is also called the "Balance of Payments Sectors".
In The Circular Flow Of Goods And Services, What Does The Product Market Represent?,
Source: https://www.economicsdiscussion.net/circular-flow/the-circular-flow-of-economic-activity/18159
Posted by: malcolmahmand.blogspot.com


0 Response to "In The Circular Flow Of Goods And Services, What Does The Product Market Represent?"
Post a Comment